

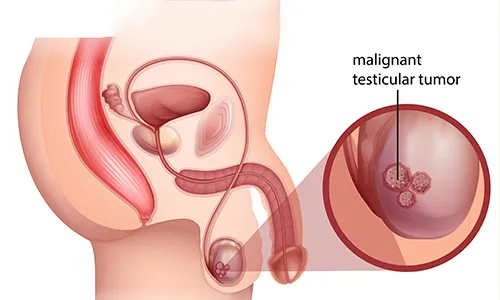
About Testicular Cancer
Testicular cancer is commonly seen in middle-aged men, with an annual incidence of four cases per lakh people. Cancer develops in the tissues of single or both testicles. Testicles are covered with a loose bag of skin known as the scrotum underneath the penis.
Testicular tumors grow in germ cells that produce sperms. Tumors of the testis are also known as testicular germ cell tumors.

Risk Factors and Prevention
Risk factors that make you susceptible to getting testicular cancer, like smoking and dietary habits, can be changed, whereas hereditary or other causes can’t.
Common risk factors:
- Undescended testicle/s
- Family history of the same
- HIV infection
- History of testicular cancer
- Body size, race, and ethnicity
- Infertility, tobacco use, etc

Screening for Testicular Cancer
Most testicular cancers can be cured at any stage of the disease. Generally, people find a lump on the testicle themselves during self-exam or by a doctor at a routine physical evaluation.
Therefore, testicular cancer does not have a routine or standard screening process for early detection.
However, early detection allows easier treatment and faster recovery, and it does not spread to another part of the body and requires less chemotherapy, surgery, and fewer side effects. So, keep an eye on testicular cancer symptoms and consult a doctor for routine body check-ups.

Testicular Cancer Symptoms & Signs
- A painless pea-sized lump or swelling on the sides of the testicles
- Heaviness and swelling of the scrotum
- Uncomfortable feeling or pain in the scrotum or testicle
- Pain in the groin, lower stomach, and the back
- Fluid in the scrotum
- Tender or enlarged breast tissue

Diagnosis and Treatment
Doctors perform the following tests if any lump or symptoms of testicular cancer are found:
- Ultrasound Scan of the scrotum to detect the location and nature of the lump on a testicle.
- Tumor marker test to check elevated levels of HCG, AFP and LDH in the bloodstream.
- A biopsy is the removal of a piece of tissue for microscopic examination.
- Doctors can also conduct surgery to remove the testicle and check for cancer.
On finding testicular cancer, doctors conduct X-Rays, and CT scans to analyze the status of cancer.
Note: All lumps are not cancerous; they could be due to multiple other reasons. Consult your doctor to confirm.

Treatment Procedure and Modalities
a. Surgery
- High Inguinal Orchiectomy
- Retroperitoneal Lymph Node Dissection
b. Radiation Treatment for Testicular Cancer
c. Chemotherapy
d. Chemotherapy with Stem Cell Transplant

Sub Types and Stages
Germ cell tumour is the most common type of testicular cancer.
Two types of GCT:
- Seminoma Testicular Cancer: It grows slowly and is common in people in their 40s and 50s.
- Nonseminomatous Germ Cell Tumour: It is related to infertility condition in men due to low sperm motility, fewer sperm counts, and abnormal morphology.
Two types of stromal tumours are Leydig cell tumours and Sertoli cell tumours.
Stages of Testicular Cancer:
- Stage 1
- Stage 2
- Stage 3
- Stage 4

Life After Testicular Cancer Treatment
- After treatment, follow-up appointments are scheduled for the next five to ten years. You will be called after every two to three months during the first three years.
- After three years, appointments are scheduled every six to twelve months.
- Doctors analyze and ask about any side effects post-treatment. They physically examine the patient and ensure they are coping well.
- Blood tests, x-rays, and CT scans are part of follow-up check-ups.
- Checking for the signs of recurrence.


FAQs
-
Do men become infertile after testicular cancer treatment?
The treatment can reduce fertility; hence sperm banking is advised before the start of therapy.
-
Will I be able to father my child after testicular cancer treatment?
Testicular cancer treatment affects hormones and might create difficulty in fathering a child. Consult your doctor about the side effects and procedure.
-
Where does Testicular Cancer spread to?
Testicular cancer can reach distant body parts in advanced stages.
-
What are the side effects of chemotherapy during testicular cancer?
Common side effects of chemotherapy in testicular cancer:
- Probability of infection
- Fatigue and mouth sore
- Bleeding and bruising
- Diarrhea and constipation
- Hair loss and lower appetite
- Vomiting and nausea
-
Is testicular cancer deadly?
Testicular cancer has one of the highest survival rates among other cancers. If diagnosed and treated on-time under expert medical supervision, there are higher chances of faster recovery.
Specialized Doctors at M | O | C
Find the nearest center
Cancer Centres
Mumbai
Pune
Rest of Maharashtra
Gujarat
Delhi NCR
Cancer Clinics
Borivali
+91 9920767626
Book Your Appointment



























.png)









.png)




















.png)
.png)
.png)



