
About Thyroid Cancer
According to various studies, more than 42 million people have thyroid cancer in India, which has become a prominent cancer form. The thyroid gland is below Adam’s Apple and secretes hormones to regulate heart rate, metabolism, bone development and body temperature.
Cells of Thyroid Gland:
- Follicular Cells
- Parafollicular or C Cells
- Immune System Cells or Lymphocytes
- Stromal Cells
Thyroid gland cancer can develop from these cells, like follicular thyroid cancer, papillary thyroid cancer, anaplastic thyroid carcinoma, medullary thyroid carcinoma etc.

Causes of Thyroid Cancer
- Three out of four Thyroid cancer patients are females. Thyroid cancers are more common in women.
- People between 20 to 55 years are more at risk for thyroid cancer.
- Some thyroid cancers happen due to gene alterations that run in the family.
- Precancerous polyps in the colon aggravate the chances of papillary thyroid cancer.
- Exposure to radiation at the head and neck increases the chances of follicular thyroid cancer and papillary thyroid carcinoma.
- Use of radiation for therapy in lymphoma disease on the head and neck.
- Any level and type of radiation exposure can cause thyroid carcinoma.
- Diet with low iodine and a history of enlarged thyroid or goitre.
- Race and ethnicity.

How can it be prevented
- Avoid radiation as much as possible, including unnecessary medical imaging
- Keep track of gene mutations in familial medullary thyroid cancer with genetic tests
- Consult a specialist doctor for the latest in genetic counselling and genetic tests
- Self-checks and screening
- Thyroid ultrasound
- Eat healthy iodine-rich food


Screening
- Thyroid cancer is usually found during self-checks, ultrasound for other conditions, or checking lumps or swelling on the neck during regular check-ups.
- Nodes on the thyroid gland can also be noticed during surgery for other conditions.

Symptoms & Signs of Thyroid Cancer
Several types of thyroid cancers do not show symptoms and signs at an early stage.
Symptoms start as cancer grows like:
- A node on the thyroid gland can be felt on the side of the neck
- Hoarseness of voice
- Difficulty swallowing and swelling in the neck
- Too much pain in the throat and neck
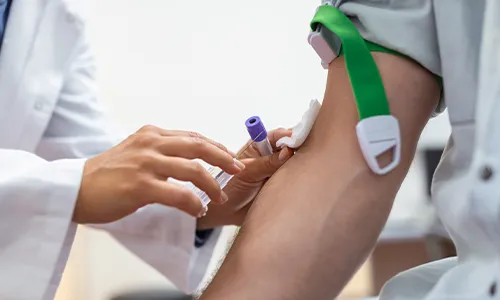

Diagnosis
Diagnosis of thyroid cancer includes following tests and procedures:
- Physical examination of neck to check lumps. They will ask about family history and other risk factors.
- Blood tests to check blood levels in TSH and hormones generated from the thyroid gland.
- Ultrasound imaging on the lower part of the neck.
- Fine needle aspiration biopsy to extract some cells from the thyroid for specialised testing.
- Radioactive iodine scan with a special camera to detect cancer cells in the body.
- MRI, CT scan, Ultrasound, and other required imaging tests.
- Genetic testing for medullary thyroid cancer, follicular thyroid carcinoma, etc.

Types and Staging
Four types of thyroid cancer:
- Papillary Thyroid Cancer
- Follicular Thyroid Cancer
- Anaplastic Thyroid Cancer
- Medullary Thyroid Cancer
Thyroid Cancer Stages
Doctors determine the stage based on diagnostic imaging.
Staging is denoted with a number between 1 and 4. Here 1 is the first stage with higher chances of recovery, and 4 is an advanced stage where cancer has spread to other body parts. Anaplastic and medullary thyroid cancers have different stages. Follicular and papillary thyroid carcinoma treatment has its own set of stages.
Stages also vary according to the age of the patient.


Treatment Modalities for Thyroid Cancer
Six treatment procedures for thyroid cancers:
a. Surgery
It involves one or more of the following procedures:
- Lobectomy
- Near-total Thyroidectomy with or without Neck Node Dissection
- Total Thyroidectomy with or without Neck Node Dissection
b. Internal and external radiation therapy with radioactive iodine procedure
c. Chemotherapy
d. Thyroid hormone replacement therapy
e. Targeted therapy
- Tyrosine kinase inhibitor
f. Immunotherapy stimulates the immune system to defend against cancer

Post Treatment Support
Palliative or supportive care is part of thyroid cancer treatment. It helps cope with cancer treatment’s mental, physical, social, and emotional impact.
Follow-ups and Cancer Care Plan:
- Ask your doctor for a follow-up plan and never miss a day as cancer has a high chance of recurrence.
- Stay attentive to any signs and symptoms.
- Doctors will tell you probable side effects and other things to take care of post-treatment in the maintenance phase.
- Follow-up appointments include physical evaluation and tests to keep track of recovery.
- You might have to visit a doctor every six months to a year for check-ups.


FAQs
-
What is papillary carcinoma?
Papillary carcinoma (PTC) is the most common differentiated thyroid gland cancer.
-
What are thyroid cancer symptoms in women?
Thyroid cancer is more prevalent among women. Refer to the symptoms sections above in the passage.
-
What is medullary carcinoma?
Medullary carcinoma is a type of thyroid cancer. It grows in the C Cell of the thyroid gland.
-
What is anaplastic carcinoma?
Anaplastic carcinoma is also known as undifferentiated thyroid carcinoma. It is an aggressive and rare thyroid tumour. It is deadly and considered one of the most dangerous cancers.
-
What is follicular carcinoma?
Follicular carcinoma and follicular adenoma are thyroid tumours generated in follicular cell differentiation. It is a benign encapsulated tumour in the thyroid gland.
Specialized Doctors at M | O | C
Find the nearest center
Cancer Centres
Mumbai
Pune
Rest of Maharashtra
Gujarat
Delhi NCR
Cancer Clinics
Borivali
+91 9920767626
Book Your Appointment



























.png)









.png)




















.png)
.png)
.png)




