
About Liver Cancer
Cancer develops in the cells of the liver. Metastatic cancer, as opposed to liver cancer, refers to cancer that starts in another part of the body which then spreads to the liver.


Risk Factors & Prevention
Adults over 60 are most likely to get primary liver cancer. Men are more likely than women to develop liver cancer.
Some of the risk factors of liver cancer are:
- Cirrhosis
- Obesity
- Diabetes
- Viral hepatitis
- Metabolic diseases
How can it be prevented?
- Avoid hepatitis B and C infections / Get vaccinated against Hepatitis B
- Limit the use of alcohol and tobacco
- Avoid obesity & stay healthy
- Treat Inherited diseases

Screening
People having a chance to get cirrhosis must get themselves regularly screened.
- Blood tests for alpha-fetoprotein
- Ultrasound
- CT scan
- MRI


Symptoms & Signs
- Pain specifically, in the top right corner of the abdomen
- Unaccounted-for weight loss
- Decreased Appetite
- On the right side of the torso, hard bump under the ribs.
- Weakness or exhaustion
- Jaundice

Diagnosis
Different Types of tests are conducted by doctors for different signs and symptoms:
- Physical examination
- Imaging tests
- Biomarker testing
- Biopsy
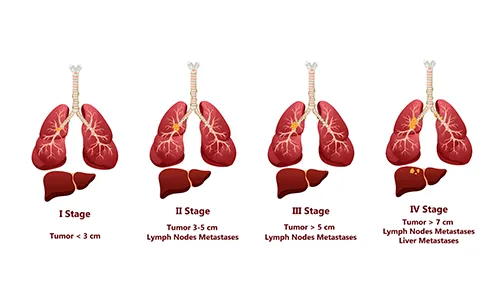

Stages
- Very early stage: Tumor smaller than 2 cm
- Early stage. Tumor: smaller than 5 cm
- Intermediate stage: Tumor may be large, or there may be multiple tumors.
- Advanced stage: Other organs have been affected by the tumor

Treatment Modalities
a. Surgery
- For tumors that are limited to one part of the liver, surgery for liver cancer is typically the treatment of choice. Like Preoperative portal vein embolization and minimally invasive procedures. Resection and lobectomy, ALPPS procedure, & Robotic surgery.
b. Liver Transplant
- It is a type of surgery where a diseased liver is replaced with a healthy liver from another person called a donor.
c. Ablation
- It is a procedure that involves the killing of cancer cells using heat, microwaves, laser or radiation therapy.
d. Embolization
- It is a procedure that blocks off the blood vessel that sends blood to cancer cells. This keeps the cancer from growing. Sometimes the embolization procedure is combined with chemotherapy (chemoembolization) or radiation (radioembolization).
e. Medical Treatment
- In order to reach cancer cells throughout the body during therapy, medication may be injected into the bloodstream (systemic treatment).
Advanced liver cancer is treated with a variety of drugs, including:
- Targeted therapy
- Immunotherapy
f. Radiation
- Radiation therapy for liver cancer uses highly focused, high-energy photons to reduce tumors and kill malignant cells.


Coping with Treatment
Along with the medical side effects of Liver cancer therapy, patients also deal with the financial burden of cancer care and the emotional and social impacts. MOC provides facility of psycho Onco-Counseling and Nutritional counseling to help patients.


Do’s & Don’ts During Treatment
Do’s
- Keep the body well hydrated
- Maintain optimal weight
- Eat small meals
Don’ts
- Avoid alcohol & tobacco
- Avoid fatty meats


Post-Treatment Support
Post-treatment Liver cancer survivors can go through long-term side effects of treatment, and long-term and late consequences may follow from physical and emotional changes. Survivors should talk with people who already have this cancer.

Follow-ups Cancer Care Plan
Post-treatment, one must request a follow-up treatment plan. Doctors provide a personalized treatment plan based on the type and stage of cancer.


Surveillance and monitoring for Signs & Symptoms
Cancer recurrence is a key concern for cancer survivors, with other health issues. Your treatment options, should the cancer return at any point, will be determined by the location of the disease, the previous treatments you underwent, and your general health.


FAQs
-
Symptoms would liver cancer have?
Fatigue, jaundice (a skin-coloring condition), abdominal pain, easy bruising or bleeding, and weight loss
-
Methods of diagnosing Liver Cancer?
Ultrasound, CT scan, MRI, Biopsy
Specialized Doctors at M | O | C
Find the nearest center
Cancer Centres
Mumbai
Pune
Rest of Maharashtra
Gujarat
Delhi NCR
Cancer Clinics
Borivali
+91 9920767626
Book Your Appointment



























.png)









.png)




















.png)
.png)
.png)



